Project I: Air Pollution PM2.5 Forecasting
Abstract
Tackling climate change and alleviating air pollution emerge as the top agendum of the global community, so we are interested in studying pollution-related time series data to look for some insights. The data we are looking into is PM2.5 data of five Chinese cities provided by the UCI Machine Learning Repository. PM2.5, referring to atmospheric particulate matter with less than 2.5 micrometer, is one of the common pollutants from power plants and automobiles. It poses risk to the human’s respiratory and heart system if the person is extensively exposed to high concentration of PM2.5. The data set includes the data of PM2.5 concentration over the period of January 1, 2010 and December 31, 2015 in the cities of Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhuo, Shenyang, and Chengdu. Some climatological data like temperature, humidity, pressure, wind direction and speed, and precipitation are also included.
Objectives
- Applied preliminary analyses to detect the seasonality and analyze the pattern of the distribution of the data each year.
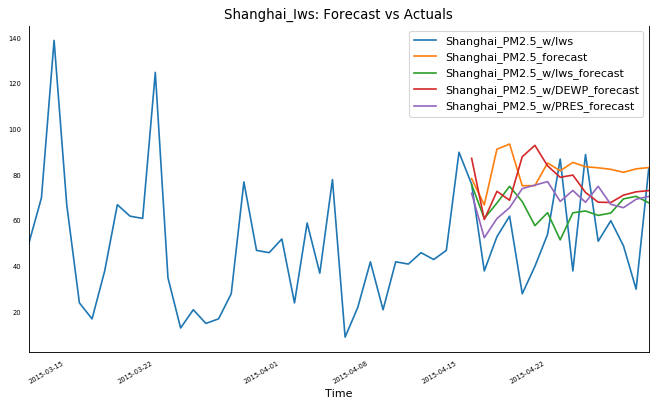
- Utilized univariate time series analysis(ARIMA/SARIMA, LSTM, Prophet) to predict the air pollution level based on past two years' weekly air quality.
- Used multivariate time series analysis(VAR) to explore the potential relationship of the PM2.5 pollution among five cities and other climatological factors.