Project III: Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Problem Statement
Diabetes is a set of diseases characterized by the body’s inability to produce or respond to insulin, used to process carbs from food. According to the CDC in 2020, just over 1 in 10 Americans have diabetes (“National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2020.”)
Blood glucose monitoring is essential for diabetes management. With modern technology, patients with diabetes can continually monitor their blood glucose levels and adjust insulin doses, striving to keep blood glucose levels as close to normal as possible. Blood glucose levels that deviate from the normal range can lead to serious short-term and long-term complications. An automatic prediction model that warns people of imminent changes in their blood glucose levels would enable them to take preventive action. Further, automatic detection can enable automatic insulin delivery, lifting this burden from the patient.
Objectives
- Diagnosed whether a patient has diabetes by analyzing relevant features data from Pima Indians Diabetes Database provided by Kaggle using logistic regression, KNN, Naive Bayes.
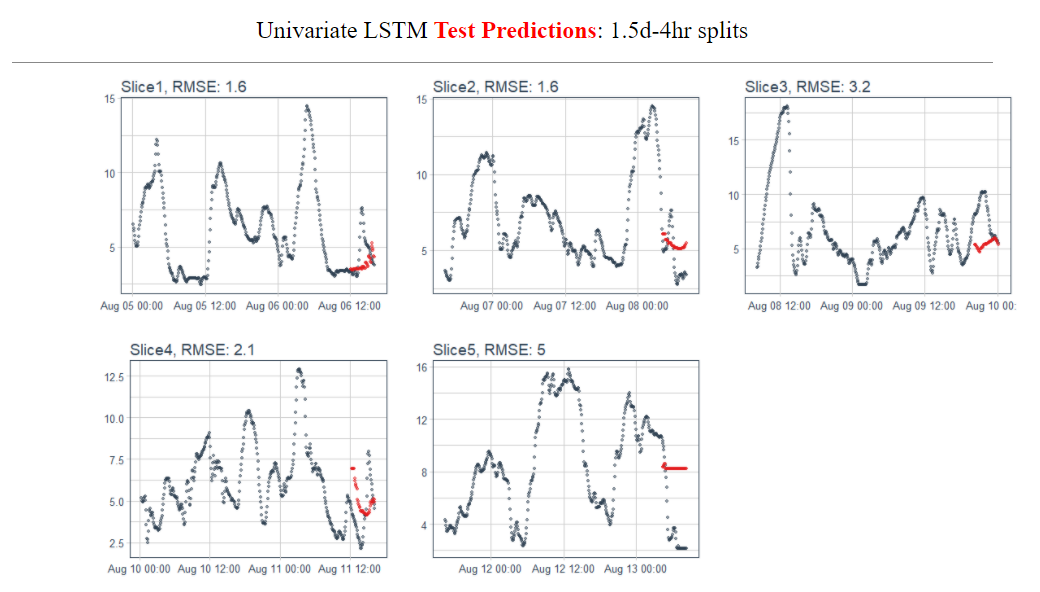
- Utilized univariate/multivariate time series analysis(ARIMA/SARIMA, VAR, Prophet, LSTM) to forecast the following forty minutes and four hours long blood glucose levels of data from the Tidepool dataset.